Osteoporosis
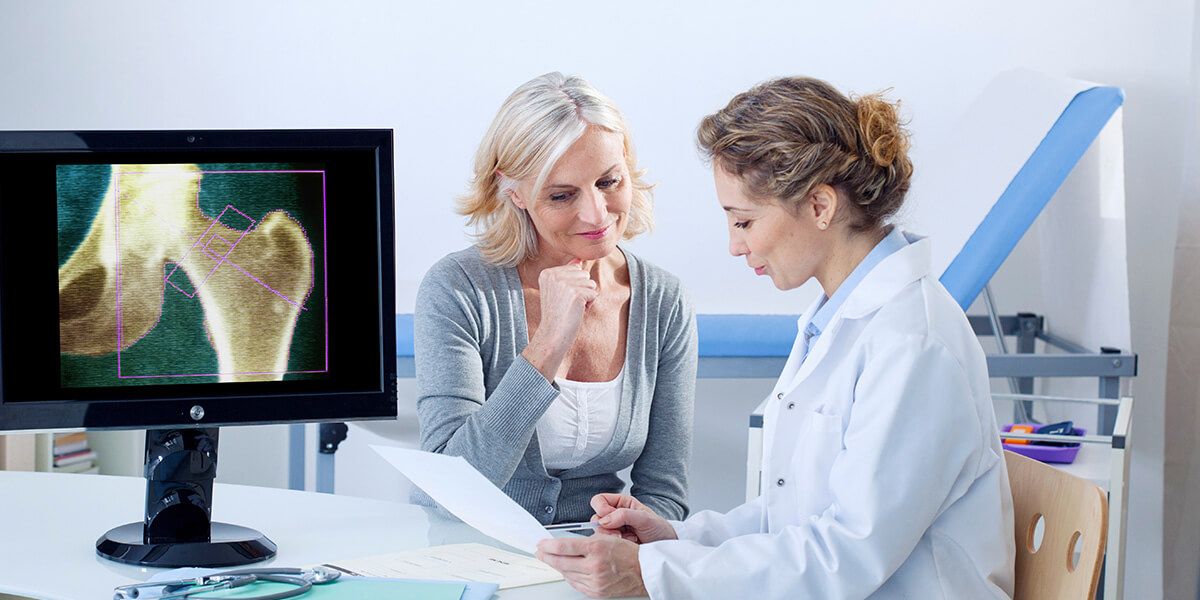
Osteoporosis is a disorder characterized by progressive weakening of the bones over time leading to an increased risk of fracture. It most commonly affects post-menopausal women but it can affect males and females equally when it is due to another underlying disease, such as vitamin D deficiency. Routine screening by your primary care provider using DEXA scans can diagnose this condition.
Osteoporosis is associated with fragility fractures involving the vertebrae, wrist, and hip. Unfortunately, it is often diagnosed after a fracture as it has no preceding symptoms. This is why routine screening by your primary care provider is crucial. Please expect secondary causes of osteoporosis to be ruled out by your physician with bloodwork that checks renal function, thyroid function, vitamin D level, parathyroid hormone, certain malignancies such as multiple myeloma and testosterone levels in male patients.
Treatment
-
Weight bearing exercise
-
Strength training
-
Calcium and vitamin D supplementation
-
Medicines that stop bone breakdown such as Fosamax, Boniva, Actonel
-
Medicines that build bone such as forteo and Prolia
-
Avoidance of medicines that can cause osteoporosis such as prednisone
In patients with osteoporosis it is imperative to minimize fall risk as there is a very high mortality in elderly patients who undergo hip fracture. These include using appropriate assistive devices such as walkers when needed and hip protectors.
Our Specialties
Our Location
Panama City
2232 W. 24th Street
Panama City, FL 32405
M-Th: 8am-Noon & 1pm-5pm
Friday: 8am-1pm
Closed For Lunch
850-215-3062 Phone
850-215-3024 Fax
